

FoAR是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 A&HCI / CSCD / Scopus / DOAJ 收录
Frontiers of Architectural Research(建筑学研究前沿 / FoAR)于9月初出版了2022年第五期。其中,《以人为本的城市设计》专辑(包含1篇《编者按》与5篇论文),以及其余9篇研究性论文。本期推送为《以人为本的城市设计》专辑中一篇文章的摘要和大纲,内容采用中文表达,方便大家阅读。推文内容不可直接引用。感兴趣的读者,请点击文末左下方“阅读原文”,可免费浏览及下载原版英文论文。

01 论文题目 Manuscript Title
The influence of calculation error of hourly marine meteorological parameter on building energy consumption calculation
逐时海洋气象参数的计算误差对建筑能耗计算的影响
02 作者 Authors
Dalong Liu*, Tian Sun, Yufei Han, Xiuying Yan
School of Architecture, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an 710055, China
03 论文摘要 Abstract
The ocean is a crucial area for future economic development. The marine environment has high energy-efficient and ecological requirements for building construction. Meteorological parameters are the key basis for the analysis and design of building energy efficiency.The lack of meteorological parameters for energy efficiency, particularly hourly data, under oceanic climatic conditions is a universal problem. The appropriate calculation methods of hourly meteorological parameters under oceanic climatic conditions are explored in this study. The impact of the calculation errors of the hourly meteorological parameters on building energy consumption is also analyzed. Three key meteorological parameters are selected: temperature, humidity, and wind speed. Five hourly calculations methods, including linear interpolation, cubic spline interpolation, pieceated three-Hermite interpolation, Akima interpolation, and radial basis function interpolation, are selected to calculate the error of the difference method, with Xiamen, Haikou, and Sanya as the locations of meteorological research. Appropriate interpolation methods are selected for the three parameters, and the seasonal and regional characteristics of the errors of each parameter are compared. Different interpolation methods should be selected for different meteorological parameters in different seasons. The error data of the three parameters of different magnitudes are constructed. A quantitative relationship between the sum of squares due to error of the three meteorological parameters and the rate of change of cooling energy consumption is established. The hourly calculation errors of meteorological parameters have an important impact on the calculation of dynamic energy consumption. The energy consumption differences caused by the errors of different parameters are significant. Obvious regional and seasonal differences also exist. This research strengthens the research foundation of building energy consumption calculation under oceanic climate conditions.
海洋是未来经济发展的关键领域。海洋环境对建筑营造有着较高的节能环保要求。气象参数是建筑节能分析和设计的重要依据。在海洋气候条件下,缺乏有效的气象参数,特别是逐时气象数据,这是一个普遍存在的问题。本研究探讨了海洋气候条件下适宜的逐时气象参数计算方法,分析了逐时气象参数计算误差对建筑能耗的影响。选取了三个重要的气象参数:温度、湿度、风速,选择了线性插值、三次样条插值、分段三次埃尔米特插值、阿克玛插值、径向基函数等5种计算方法,以厦门、海口、三亚为研究地点来分析不同方法之间的误差。本文针对这三个参数选择了合适各自的插值方法,对不同季节和区域特征下的各个参数之间的误差进行了比较。发现不同气象参数在不同季节应选择不同的插值方法。构建了三个参数不同量级的误差数据,建立了三个气象参数的误差指标和与空调能耗变化率之间的定量关系。发现气象参数的逐时计算误差对动态能耗计算有着重要的影响。不同量级参数误差引起的能耗存在显著差异,同时该影响也存在明显的地域和季节差异。本文深化了海洋性气候条件下建筑能耗计算的研究基础。
04 关键词 Keywords
Building energy efficiency / 建筑能效
Oceanic climate / 海洋性气候
Meteorological parameters / 气象参数
Interpolation method / 插值法
Calculation error / 计算错误
Dynamic energy simulation / 动态能源模拟
05 章节标题 Sections Title
1. Introduction / 引言
2. Methodology / 研究方法
2.1. Method of hourly interpolation / 逐时插值法
2.2. Error analysis method / 误差分析方法
2.3. Data sources and analysis sites / 数据资源及分析地点
2.4. Energy consumption simulation settings / 能耗模拟设置
3. Comparative analysis of the hourly calculation methods of marine meteorological parameters / 海洋气象参数的逐时计算法比较分析
3.1. Temperature / 温度
3.2. Relative humidity / 相对湿度
3.3. Wind / 风
3.4. Comparative analysis of the experimental results of different meteorological parameters / 不同气象参数实验结果的比较分析
4. Dynamic simulation of building energy consumption under sea climate / 海洋性气候下建筑能耗的动态模拟
4.1. Error variation method of meteorological parameters / 气候参数的误差变异法
4.2. Overview of building energy consumption simulation / 建筑能耗模拟综述
5. Influence of the hourly error of marine meteorological parameters on building energy consumption calculation / 海洋性气象参数的逐时误差对建筑能耗计算的影响
5.1. Influence on hourly energy consumption calculation / 对逐时能耗计算的影响
5.2. Influence on the calculation of daily total energy consumption / 对每日总能耗计算的影响
6. Conclusions / 结论
06 主要插图 Illustrations
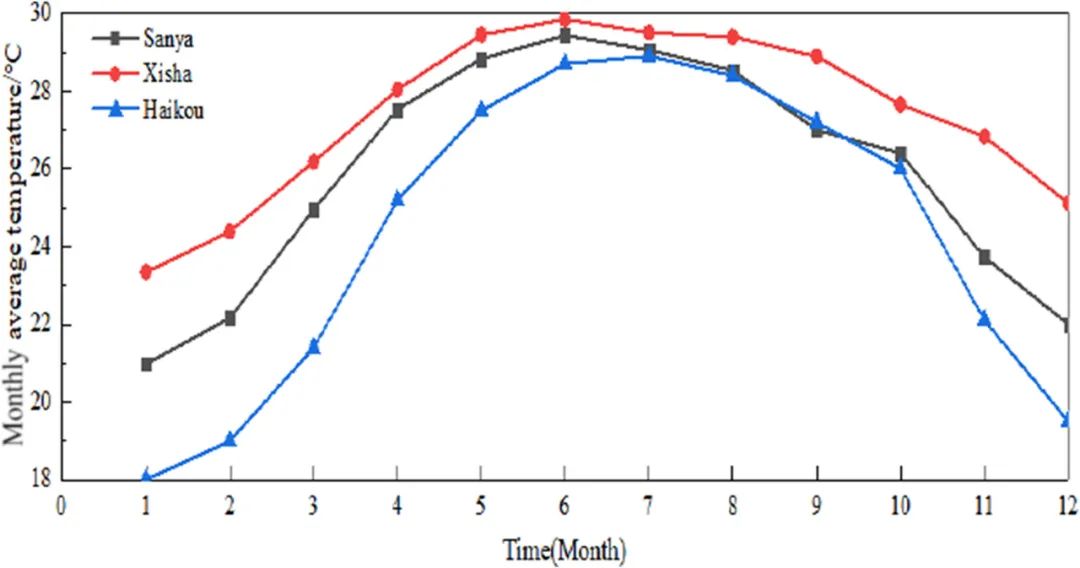
▲ 图一:三亚、西沙、海口三座城市月平均气温比较。© 本文作者
▲ 图二:建筑模型。© 本文作者
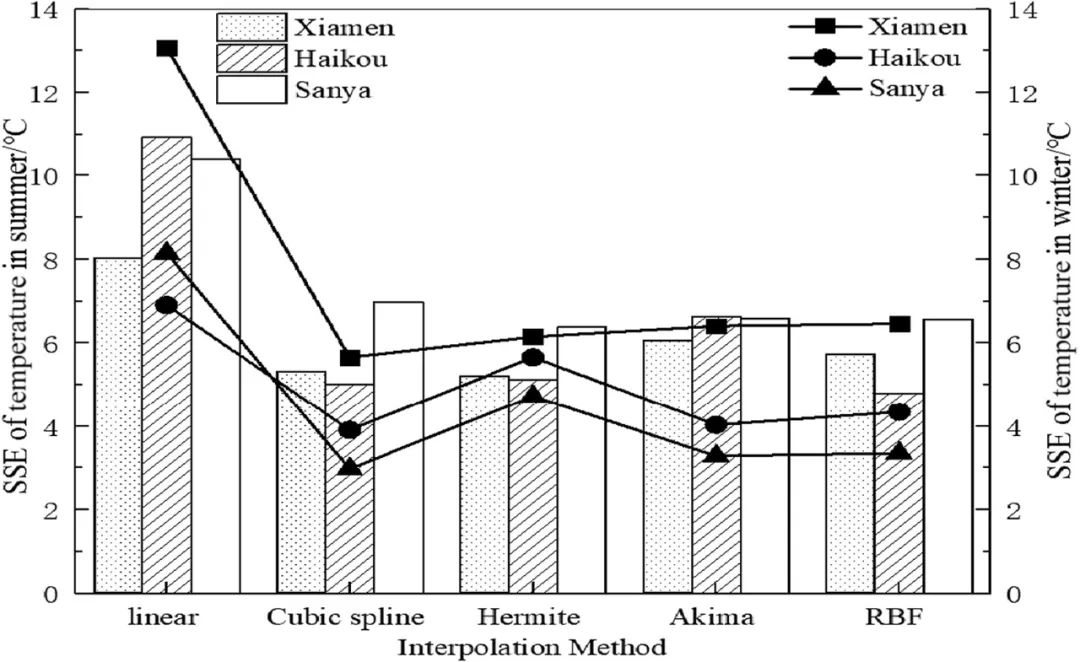
▲ 图三:温度插值的误差平方和。© 本文作者

▲ 图四:温度插值的R2指数。© 本文作者
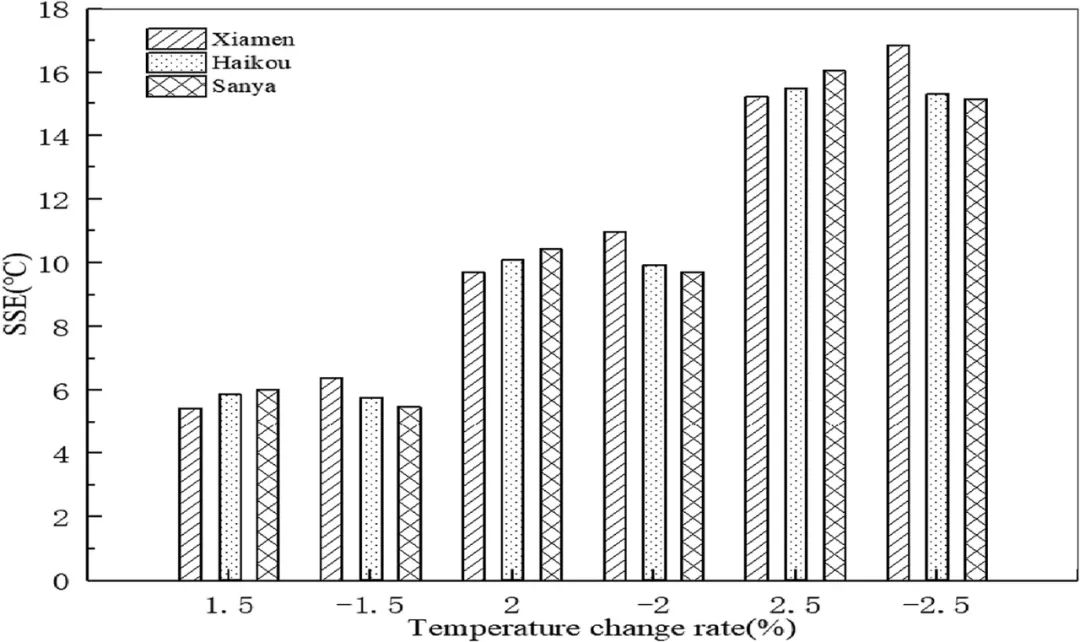
▲ 图五:温度变化率与误差平方和的对应关系。© 本文作者
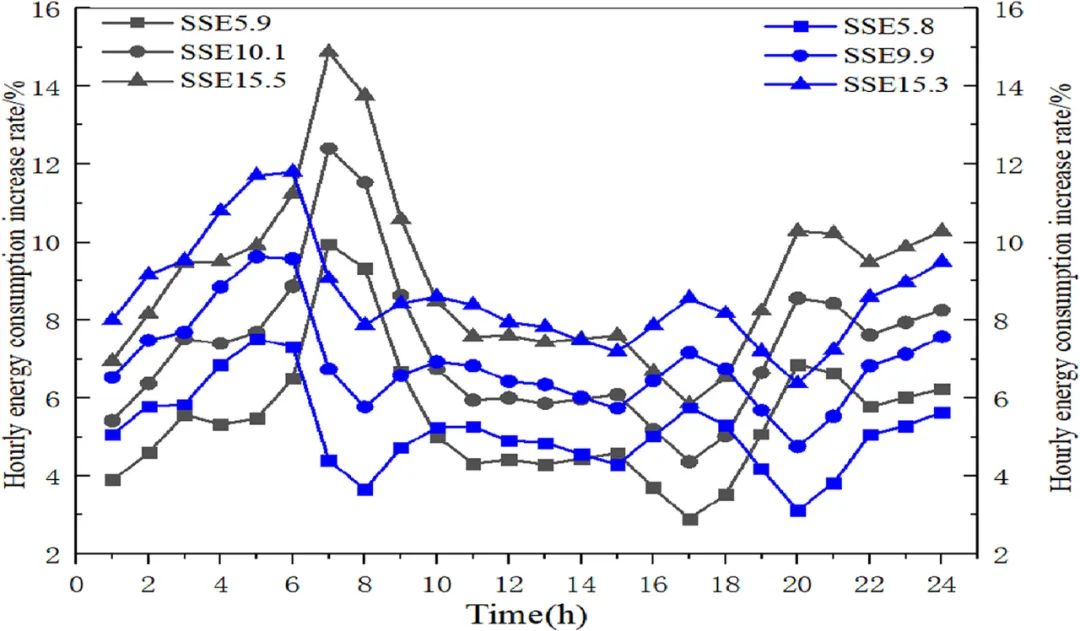
▲ 图六:海口市气温的误差平方和与逐时能耗之间的关系。© 本文作者
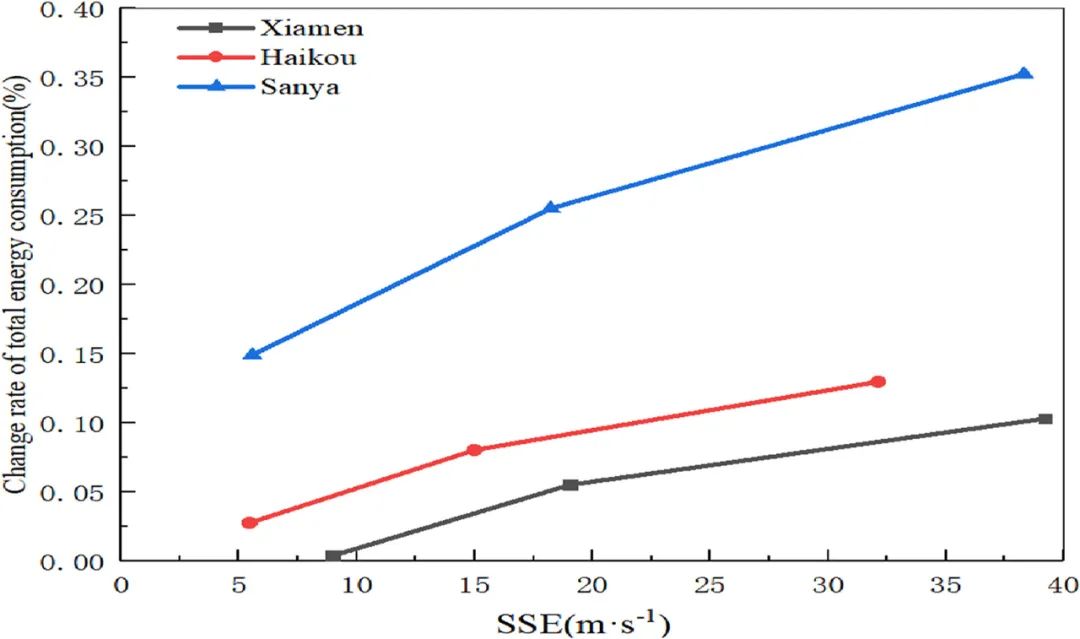
▲ 图七:风速的误差平方和与总能耗之间的关系。© 本文作者
07 作者介绍 Authors Information

刘大龙
副教授
西安建筑科技大学,建筑学院
研究方向:建筑热工与节能

孙 恬
硕士研究生
西安建筑科技大学,建筑学院
研究方向:建筑热工

韩雨菲
硕士研究生
西安建筑科技大学,信息与控制工程学院
研究方向:节能气象参数

闫秀英
副教授
西安建筑科技大学,建筑设备科学与工程学院
研究方向:建筑智能化与节能调控
08 原文阅读 Download Link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
期刊联络
刊物邮箱:foar@pub.seu.edu.cn
FoAR英文期刊交流QQ群:21608832
在线投稿
www.editorialmanager.com/foar
刊物主页
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/20952635
http://journal.hep.com.cn/foar


《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。

文章中观点仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本网站的观点和看法。
神州学人杂志及神州学人网原创文章转载说明:如需转载,务必注明出处,违者本网将依法追究。